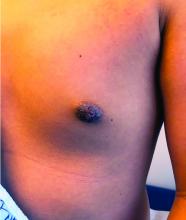
Nipple eczema is a dermatitis of the nipple and areola with clinical features such as erythema, fissures, scaling, pruritus, and crusting.1,2 It is classically associated with atopic dermatitis (AD), though it may occur as an isolated condition less commonly. While it may affect female adolescents, nipple eczema has also been reported in boys and breastfeeding women.3,4 The overall risk of incidence of nipple dermatitis has also been shown to increase with age.5 Nipple eczema is considered a cutaneous finding of AD, and is listed as a minor diagnostic criteria for AD in the Hanifin-Rajka criteria.6 The patient had not related his history of AD, which was elicited after finding typical antecubital eczematous dermatitis, and he had not been actively treating it.
Diagnosis and differential
Nipple eczema may be a challenging diagnosis for various reasons. For example, a unilateral presentation and the changes in the eczematous lesions overlying the nipple and areola’s varying textures and colors can make it difficult for clinicians to identify.3 Many children and adolescents, including our patient, are initially diagnosed as having impetigo and treated with antibiotics. The diagnosis of nipple eczema is made clinically, and management straightforward (see below). However, additional testing may be appropriate including patch testing for allergic contact dermatitis or bacterial cultures if bacterial infection or superinfection is considered.7,8 The differential diagnosis for nipple eczema includes impetigo, gynecomastia, scabies, and allergic contact dermatitis.
Impetigo typically presents with honey-colored crusts or pustules caused by infection with Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus. Patients with AD have higher rates of colonization with S. aureus and impetiginized eczema in common. Impetigo of the nipple and areola is more common in breastfeeding women as skin cracking from lactation can lead to exposure to bacteria from the infant’s mouth.9 Treatments involve topical or oral antibiotics.
Gynecomastia is the development of male breast tissue with most cases hypothesized to be caused by an imbalance between androgens and estrogens.10 Some other causes include direct skin contact with topical estrogen sprays and recreational use of marijuana and heroin.11 It is usually a benign exam finding in adolescent boys. However, clinical findings such as overlying skin changes, rapidly enlarging masses, and constitutional symptoms are concerning in the setting of gynecomastia and warrant further evaluation.
Scabies, which is caused by the infestation of scabies mites, is a common infectious skin disease. The classic presentation includes a rash that is intensely itchy, especially at night. Crusted scabies of the nipples may be difficult to distinguish from nipple eczema. Areas of frequent involvement of scabies include palms, between fingers, armpits, groin, between toes, and feet. Treatments include treating all household members with permethrin cream and washing all clothes and bedding in contact with a scabies-infected patient in high heat, or oral ivermectin in certain circumstances.12
Allergic contact dermatitis is a common cause of breast and nipple dermatitis and should be considered within the differential diagnosis of nipple eczema with atopic dermatitis, or as an exacerbator.7,9 Patients in particular who present with bilateral involvement extending to the periareolar skin, or unusual bilateral focal patterns suggestive for contact allergy should be considered for allergic contact dermatitis evaluation with patch tests. A common causative agent for allergic contact dermatitis of the breast and nipple includes Cl+Me-isothiazolinone, commonly found in detergents and fabric softeners.7 Primary treatment includes avoidance of the offending agents.