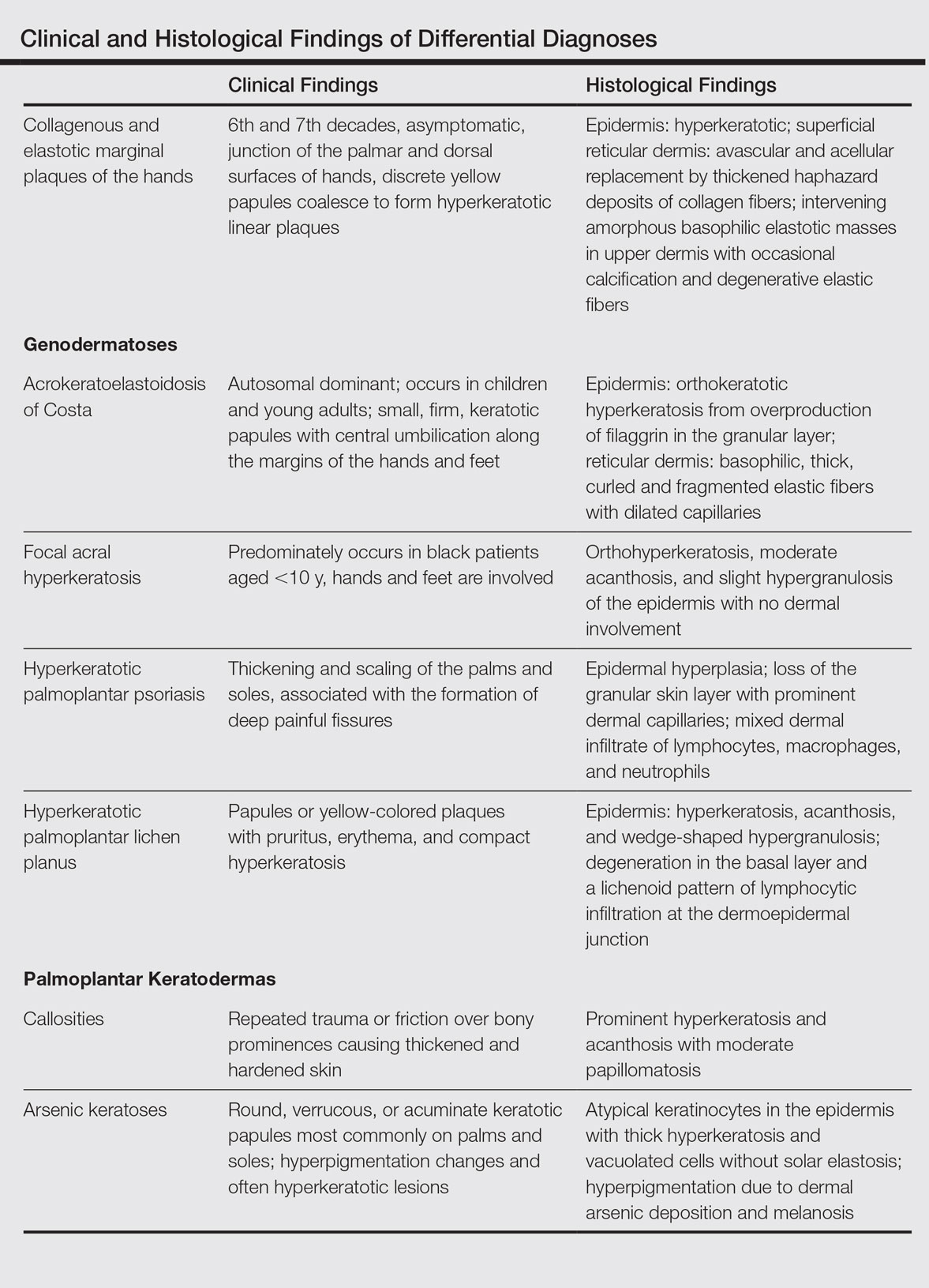
Chronic hyperkeratotic eczematous dermatitis is another common entity in the differential characterized by hyperkeratotic plaques that scale and fissure. Biopsy demonstrates a spongiotic acanthotic epidermis.7,8
Psoriasis of the hands, specifically hyperkeratotic palmoplantar psoriasis, is associated with manual labor, similar to CEMPH. Histology shows epidermal hyperplasia; regular acanthosis; loss of the granular skin layer with prominent dermal capillaries; and a mixed dermal infiltrate of lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils.9 Hyperkeratotic palmoplantar lichen planus presents with pruritic papules in the third and fifth decades of life. Histologically, hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and wedge-shaped hypergranulosis with a lichenoid lymphocytic infiltration at the dermoepidermal junction is seen.10
Palmoplantar keratodermas due to inflammatory reactive dermatoses include callosities that develop in response to repeated trauma or friction on the skin. On histology, there is prominent hyperkeratosis and acanthosis with moderate papillomatosis.11 Drug-related palmoplantar keratodermas such as those from arsenic exposure can lead to multiple, irregular, verrucous, keratotic, and pigmented lesions on the palms and soles. Histologically, atypical keratinocytes are seen in the epidermis with thick hyperkeratosis and vacuolated cells without solar elastosis.12
In conclusion, CEMPH is an underdiagnosed and underrecognized condition characterized by asymptomatic hyperkeratotic linear plaques along the medial aspect of the thumb and radial aspect of the index finger. It is important to keep CEMPH in mind when dealing with occupational cases of repeated long-term trauma or pressure to the hands as well as excessive sun exposure. It also is imperative to separate it from other diseases and avoid misdiagnosing this degenerative collagenous and elastotic disease as a malignant lesion.