The first botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) was onabotulinumtoxinA in 1989 for the treatment of strabismus and blepharospasm. It was not until 1992, however, that the aesthetic benefits of BoNT were first reported in the medical literature by Carruthers and Carruthers,1 and a cosmetic indication was not approved by the FDA until 2002. Since that time, the popularity of BoNT products has grown rapidly with a nearly 6500% increase in popularity from 1997 to 2015 in addition to the introduction of a variety of new BoNT formulations to the market.2 It is estimated by the American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery that there were at least 4,000,000 BoNT injections performed in 2015 alone, making it the most popular nonsurgical aesthetic procedure available.2 As the demand for minimally invasive cosmetic procedures continues to increase, we will continue to see the introduction of additional formulations of BoNT products as well as novel administration techniques and delivery devices. In this article, we provide an update on current and upcoming BoNT products and also review the literature on novel administration methods based on studies published from January 1, 2014, to December 31, 2015.
Current Products
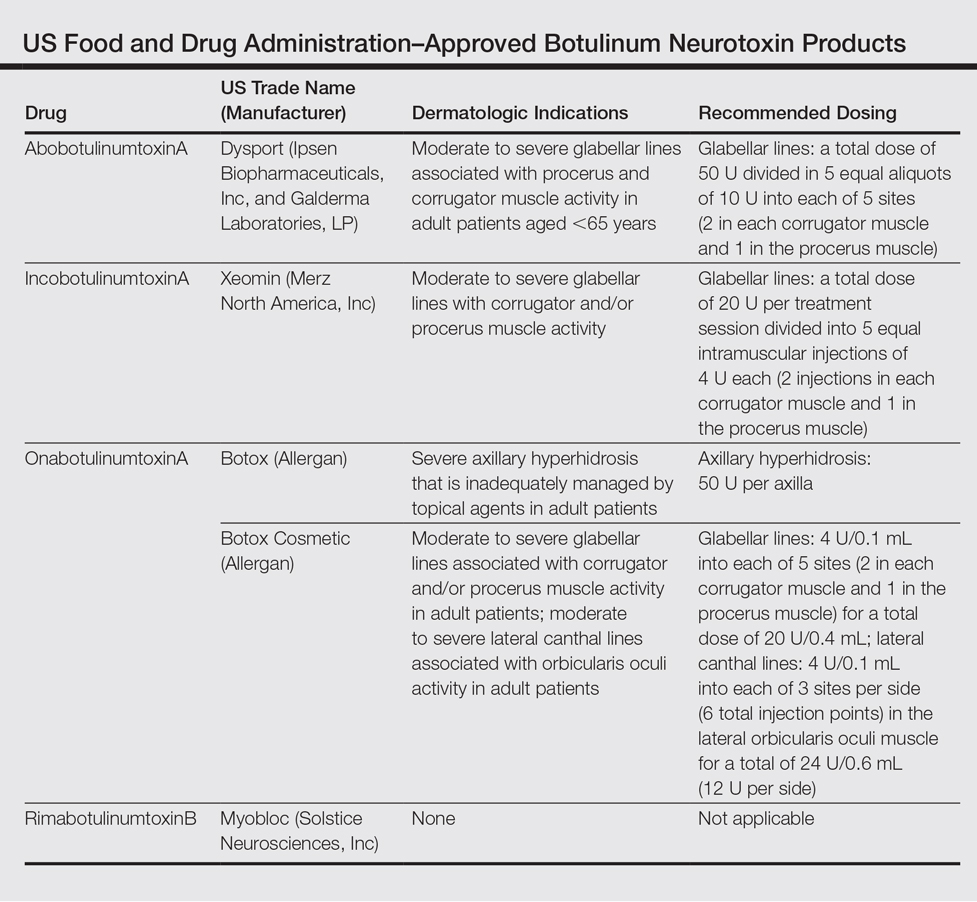
To date, there are only 4 FDA-approved formulations of BoNT available for clinical use (eg, cervical dystonia, strabismus, blepharospasm, headache, urinary incontinence) in the United States: abobotulinumtoxinA, incobotulinumtoxinA, onabotulinumtoxinA, and rimabotulinumtoxinB.The FDA-approved dermatologic indications (eg, moderate to severe glabellar or canthal lines, severe axillary hyperhidrosis) for these products are provided in the Table. On a global scale, there are several other commonly utilized formulations of BoNT, including a Korean serotype resembling onabotulinumtoxinA and a Chinese botulinum toxin type A.3 Although there is some evidence to demonstrate comparable efficacy and safety of these latter products, the literature is relatively lacking in comparison to the FDA-approved products.4,5
Upcoming Products
Currently, there are several new BoNT formulations being studied for clinical use. RT 002 (Revance Therapeutics, Inc) is a novel injectable formulation of onabotulinumtoxinA that consists of the purified neurotoxin in combination with patented TransMTS peptides that have been shown to provide high-binding avidity for the neurotoxin, and thus the product is designed to reduce diffusion to adjacent muscles and diminish unwanted effects. With a reduced level of neurotoxin dissemination, it is theorized that a higher administration of targeted doses can be injected, which may lead to a longer duration of desired effects.6 A clinical pilot study done to establish the safety and efficacy of RT 002 for treatment of moderate to severe glabellar lines evaluated 4 equally sized cohorts of 12 participants, each receiving single-dose administration of RT 002 ranging in potency equivalent to 25 U, 50 U, 75 U, and 100 U of abobotulinumtoxinA as determined by the gelatin phosphate method.6 It was concluded that RT 002 is both safe and efficacious with an extended duration of action, with a median duration of effect of 7 months observed in the highest dose group (dose equivalent to 100 U of abobotulinumtoxinA). Notably, 80% of all 48 participants maintained a minimum 1-point improvement in investigator-determined glabellar line severity scores at the 6-month time point and 60% achieved wrinkle scores of none or mild at 6 months posttreatment.6
DWP 450 (Daewoong Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd) is derived from the wild-type Clostridium botulinum and is reported to be of higher purity than standard onabotulinumtoxinA. An initial 16-week pilot study demonstrated that 20 U of DWP 450 is noninferior and of comparable efficacy and safety to 20 U of onabotulinumtoxinA in the treatment of glabellar lines.7
NTC (Botulax [Hugel, Inc]) is the name of the toxin derived from the C botulinum strain CBFC26, which has already been approved in many Asian, European, and Latin American countries for the treatment of blepharospasm. This formulation has demonstrated noninferiority to onabotulinumtoxinA at equivalent 20-U doses for the treatment of moderate to severe glabellar lines in a double-blind, randomized, multicenter, phase 3 trial of 272 participants with a 16-week follow-up.8
MT 10109L (Medytox Inc) is a unique product in that it is distributed as a liquid type A botulinum toxin rather than the standard freeze-dried formulation; thus, a major advantage of this product is its convenience, as it does not need reconstitution or dilution prior to administration. In a double-blind, randomized, active drug–controlled, phase 3 study of 168 participants, it was determined that MT 10109L (20 U) is comparable in efficacy to onabotulinumtoxinA (20 U) for the treatment of moderate to severe glabellar lines. No significant difference was seen between the 2 treatment groups when glabellar lines were assessed at rest at 4 and 16 weeks after treatment, but a significantly greater improvement in glabellar lines was seen at maximum frown in the MT 10109L group at the 16-week follow-up (P=.0064).9