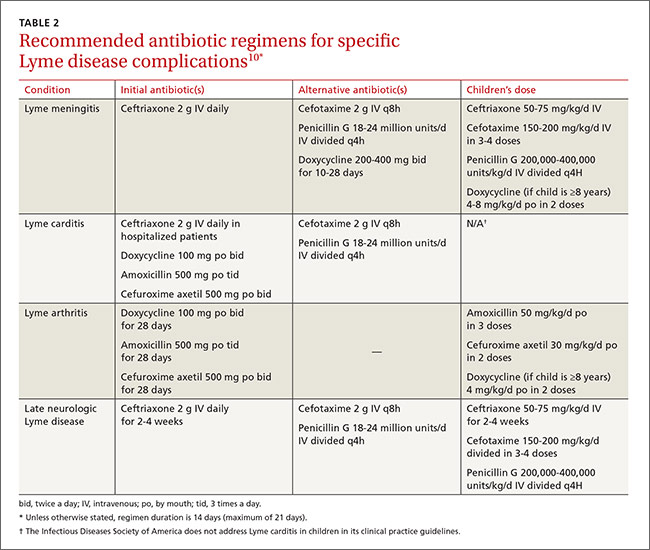
Lyme arthritis can be treated with oral doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime axetil for 28 days. For patients with persistent or recurrent joint swelling who have been treated with a course of oral antibiotics, administer an additional 4 weeks of oral antibiotics or 2 to 4 weeks of IV ceftriaxone.10 A second 4-week course of oral antibiotics is also suggested for patients whose symptoms have greatly improved but not fully resolved.3,4,7,10
For post-Lyme syndromes, antibiotics have not proved useful and are not recommended for patients with chronic (>6 months) subjective symptoms.10,16 A recent study in Europe failed to show that antibiotic treatment for 12 weeks reduced symptoms or improved quality of life in patients with persistent symptoms associated with Lyme disease.18
Prognosis: It varies with specific complications
EM resolves within a few days or weeks (up to 8 weeks) after initiation of treatment. Generally, between 70% and 85% of patients with Lyme neuroborreliosis make a complete recovery, usually 6 to 12 months after initiation of therapy; and up to 90% of patients with facial palsy recover.6 Residual neurologic complications (facial nerve dysfunction, radiculopathies, vision or hearing loss, ataxia) have been documented in 5% to 28% of patients one year after therapy. Lyme arthritis resolves spontaneously, but it can take years and may require anti-inflammatory treatment.5,6